Simple Games
- Games: a mathematical formalism for rational interaction
- What is the most popular solution concept? (Nash Equilibrium)
Types of Uncertainty
Alleatory
Epistemic (Static)
Epistemic (Dynamic)


Interaction

Markov Decision Process
Reinforcement Learning
POMDP

Game
Normal Form Games
- Alice and Bob are working on a homework assignment.
- They can either share or withhold their knowledge.
- If one player shares knowledge, the other benefits greatly, but the sharer also benefits by getting to test their knowledge
Called a Normal Form, Simple, or Bimatrix Game
Question for today: What solution concept should we use for games?
| S | W | |
| S | 4 | 2 |
| W | 3 | 1 |
A
B
Alice's Payoffs
| S | W | |
| S | 4 | 3 |
| W | 2 | 1 |
A
B
Bob's Payoffs
| S | W | |
| S | 4, 4 | 2, 3 |
| W | 3, 2 | 1, 1 |
Alice
Bob
A win-win situation: International trade
- Both Britain and Portugal need textiles and wine
- Britain:
- Producing wine: -3
- Producing textiles: -1
- Portugal:
- Producing wine: -1
- Producing textiles: -3
- No production capacity limits
- Each country can either
- Produce their own goods
- Trade at a price of 2
From 2021: This example isn't great
Dominant Strategies
- Dominant (Pure) Strategy: Action \(a\) is a dominant strategy if it is a best response to every action taken by the other player.
- Dominant Strategy Equilibrium: Every player plays a dominant strategy
Definitions
- Action \(a^i \in A^i\)
- Joint Action \(a = (a^1, \ldots, a^k)\)
- All Other Actions
\(a^{-i} = (a^1, \ldots, a^{i-1}, a^{i+1}, \ldots, a^k)\) - Reward \(R^i (a)\)
- Joint Reward \(R(a) = (R^1(a), \ldots, R^k(a))\)
Deterministic Best Response:
Action \(a^i\) is a deterministic best response to \(a^{-i}\) if \[R^i (a^i, a^{-i}) \geq R^i ({a^i}', a^{-i}) \quad \forall {a^i}'\]
Is the dominant strategy equilibrium always the best outcome for the players?
| S | W | |
| S | 4, 4 | 2, 3 |
| W | 3, 2 | 1, 1 |
Alice
Bob
A more surprising example:
The Prisoner's Dilemma
- 2 criminals are captured
- Each can either keep silent or testify
- other keeps silent -> minor conviction (1 year)
- other testifies -> major conviction: 4 years
- testify -> 1 year removed from sentence
- Dominant strategy for both players is to testify
- Dominant strategy equilibrium is a very bad social result (for the criminals)
Do all simple games have a dominant strategy equilibrium?
| S | T | |
| S | -1, -1 | -4, 0 |
| T | 0, -4 | -3, -3 |
Player 2
Player 1
Collision Avoidance Game
Pure Nash Equilibrium: All players play a deterministic best response.
Collision
Example: Airborne Collision Avoidance
|
|
|
|
|
Player 1
Player 2
Up
Down
Up
Down
-5, -5
-1, 0
0, -1
-4, -4

Collision
Do all simple games have a pure Nash equilibrium?
Which equilibrium is better?
Practice: Find Pure Nash Equilibria

Missile Defense Game
Missile Defense (simplified)
|
|
|
|
|
Attacker
Defender
Up
Down
Up
Down
-1, 1
1, -1
1, -1
-1, 1
Collision
Collision
No Pure Nash Equilibrium!
Need a broader solution concept: Mixed Nash equilibrium.
Vocabulary and Notation for Mixed Strategies
- Action \(a^i \in A^i\) \(a \in A\)
- Policy (strategy) \(\pi^i(a^i)\) \(\pi(a) = \prod_i \pi^i(a^i)\)
- Reward \(R^i(a)\) \(R(a)\)
- Utility \(U^i(\pi) = \sum_{a} R^i(a) \pi(a)\) \(U(\pi) = \sum_{a} R(a) \pi(a)\)
Single Player Joint
Best Response: Given a joint policy of all other agents, \(\pi^{-i}\), a best response is a policy \(\pi^i\) that satisfies
\[U^i\left(\pi^i, \pi^{-i} \right) \geq U^i\left({\pi^i}',\pi^{-i}\right)\]
for all other \({\pi^i}'\).
Two Player Zero Sum: \[R^1(a) + R^2(a) = 0 \quad \forall a\]
Vocabulary and Notation
- Action \(a^i \in A^i\) \(a \in A\)
- Policy (strategy) \(\pi^i(a_i)\) \(\pi(a) = \prod_i \pi^i(a_i)\)
- Reward \(R^i(a)\) \(R(a)\)
- Utility \(U^i(\pi) = \sum_{a} R^i(a) \pi(a)\) \(U(\pi) = \sum_{a} R(a) \pi(a)\)
Single Player Joint
\((R^1(A^1,A^2), R^2(A^1,B^1))\)
\((R^1(\cdot), R^2(\cdot))\)
\((R^1(\cdot), R^2(\cdot))\)
\((R^1(\cdot), R^2(\cdot))\)
\((R^1(\cdot), R^2(\cdot))\)
Nash Equilibria
Nash Equilibrium

- A Nash equilibrium is a joint policy in which all agents are following a best response
Missile Defense Game
Missile Defense (simplified)
|
|
|
|
|
Attacker
Defender
Up
Down
Up
Down
-1, 1
1, -1
1, -1
-1, 1
Collision
Collision
- A Nash equilibrium is a joint policy in which all agents are following a best response
Rock-paper scissors

Do all simple games have at least one Nash equilibrium?
Yes!! (might be mixed)
- Guess the Nash Equilibrium argument
- Make a qualitative argument that this is an NE based on best responses
Every finite game has a Nash Equilibrium



- Let \(x\) be a strategy profile, \(\pi\).
- Let \(f\) be \(BR\), that is, the best response operator
- A fixed point of \(BR\) is a Nash Equilibrium
- The \(BR\) operator and policy space for finite games meet the conditions above
- \(BR\) has a fixed point for every finite game, i.e. every finite game has a Nash Equilibrium
Calculating Mixed Nash
| Stag | Hare | |
|---|---|---|
| Stag | 4, 4 | 1, 3 |
| Hare | 3, 1 | 2, 2 |

- In a Mixed Nash Equilibrium, players must be indifferent between two or more actions
- (In large games, finding the support of the mixed strategies is the hard part)
Battle of the Sexes
- Gabby and Max are going on a date
- Gabby wants to go to a football game
- Max wants to go to a movie (He is a rom-com superfan)
Correlated Equilibrium
- A correlated joint policy is a single distribution over the joint actions of all agents.
- A correlated equilibrium is a correlated joint policy where no agent i can increase their expected utility by deviating from their current action to another.
- Easier to find than Nash equilibrium (Linear Program)
General approach to find Nash Equilibria

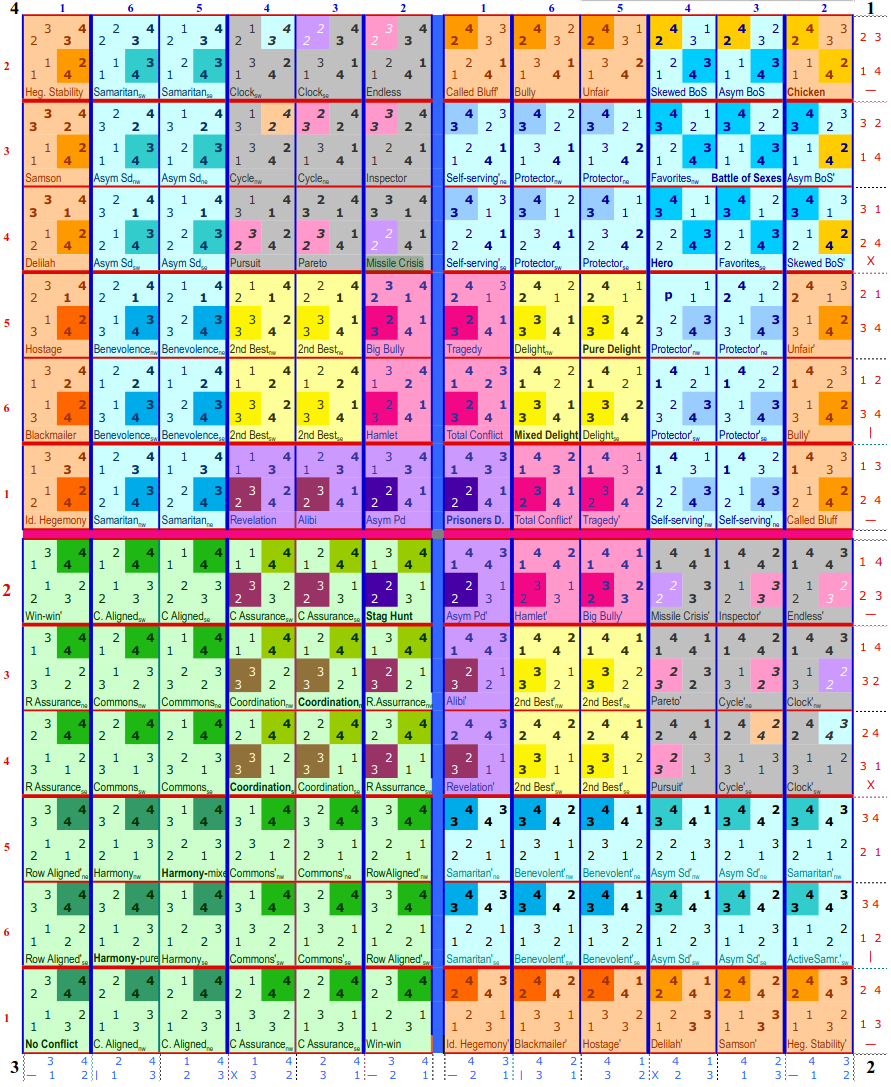
Topology of bimatrix games:
Algorithms that use best response
Iterated Best Response: randomly cycle between agents who play the best response for the current policy (converges to Nash for certain narrow classes of games)
Fictitious Play:
- Estimate maximum likelihood policies for opponents: \[\pi^j (a^j) \propto N (j, a^j)\]
- Play best response to estimated policy
(converges to Nash for wider class of games, notably zero-sum)
Battle of the Sexes
- Two people want to go to a concert
- P1 prefers Bach, P2 Stravinsky
Correlated Equilibrium
- A correlated joint policy is a single distribution over the joint actions of all agents.
- A correlated equilibrium is a correlated joint policy where no agent i can increase their expected utility by deviating from their current action to another.
- Easier to find than Nash equilibrium (Linear Program)
Bach or Stravinsky
| B | S | |
|---|---|---|
| B | 2, 1 | 0,0 |
| S | 0, 0 | 1, 2 |
Recap
- Games provide a mathematical framework for analyzing interaction between rational agents
- Games may not have a single "optimal" solution; instead there are equilibria
- If every player is playing a best response, that joint policy is a Nash Equilibrium
- Every finite game has at least one Nash Equilibrium (pure or mixed)
- Mixed Nash equillibria occur when players are indifferent between two outcomes
https://youtube.com/shorts/w3q77ZZIqwA?si=J8H6L6W5kTRs-mUx
240 Simple Games
By Zachary Sunberg
240 Simple Games
- 832



